CrowdSec WAF QuickStart for Traefik
Objectives
The goal of this quickstart is to set up the AppSec Component to safeguard web applications running on Traefik reverse proxy. We'll deploy a set of rules designed to block well-known attacks and currently exploited vulnerabilities. Additionally, we'll show how to monitor these alerts through the console.
Pre-requisites
-
If you're new to the AppSec Component or Web Application Firewalls, start with the Introduction for a better understanding.
-
It's assumed that you have already installed:
- CrowdSec Security Engine: for installation, refer to the QuickStart guide. The AppSec Component, which analyzes HTTP requests, is included within the security engine as a Acquisition.
- Traefik Plugin Remediation Component: Thanks to maxlerebourg and team they created a Traefik Plugin that allows you to block requests directly from Traefik.
AppSec Component Setup
Collection installation
To begin setting up the AppSec Component, the initial step is to install a relevant set of rules.
We will utilize the crowdsecurity/appsec-virtual-patching collection, which offers a wide range of rules aimed at identifying and preventing the exploitation of known vulnerabilities.
This collection is regularly updated to include protection against newly discovered vulnerabilities. Upon installation, it receives automatic daily updates to ensure your protection is always current.
Furthermore we also install the crowdsecurity/appsec-generic-rules collection. This collection contains detection scenarios for generic attack vectors. It provides some protection in cases where specific scenarios for vulnerabilities do not exist (yet).
- Docker
- Docker Compose
- Kubernetes (Helm)
## This command should be used when you are persisting /etc/crowdsec/ on the host
docker exec -it crowdsec cscli collections install crowdsecurity/appsec-virtual-patching crowdsecurity/appsec-generic-rules
This command installs the needed appsec hub configuration items.
services:
crowdsec:
environment:
- 'COLLECTIONS=crowdsecurity/appsec-virtual-patching crowdsecurity/appsec-generic-rules'
This compose configuration file will add some needed hub configuration items.
Please add this in your values.yaml for your CrowdSec release.
appsec:
env:
- name: COLLECTIONS
value: "[...] crowdsecurity/appsec-virtual-patching crowdsecurity/appsec-generic-rules [...]"
Now you can apply it with:
helm upgrade crowdsec crowdsec/crowdsec -n crowdsec --create-namespace -f ./crowdsec-values.yaml
This values.yaml modification will add some needed hub configuration items.
Those needed hub configuration items are:
- The AppSec Rules contain the definition of malevolent requests to be matched and stopped.
- The AppSec Configuration links together a set of rules to provide a coherent set.
- The CrowdSec Parser and CrowdSec Scenario(s) are used to detect and remediate persistent attacks.
Once you have updated your compose or installed via the command line, will we need to restart the container. However, before we do that, we need to setup the acquisition for the AppSec Component.
Setup the Acquisition
You now need to setup the acquisition for AppSec. The way it's done highly depends on how you run CrowdSec.
- Docker
- Docker Compose
- Kubernetes (Helm)
In the directory where you persist configuration files, create an appsec.yaml file and mount it into the container.
Steps
- Change to the directory where you ran the
docker runordocker composecommand. - Create a file named
appsec.yamlin this directory. - Add the following content:
appsec_config: crowdsecurity/appsec-desfault
labels:
type: appsec
listen_addr: 0.0.0.0:7422
source: appsec
Because CrowdSec runs inside a container, set listen_addr to 0.0.0.0 instead of 127.0.0.1 so it can accept connections from outside the container.
Edit your docker run command to mount the file:
If a crowdsec container is already running, stop/remove it before re-running with the updated mounts.
docker run -d --name crowdsec \
-v /path/to/original:/etc/crowdsec \
-v ./appsec.yaml:/etc/crowdsec/acquis.d/appsec.yaml \
crowdsecurity/crowdsec
In the directory where you persist configuration files, create an appsec.yaml file and mount it into the container.
Steps
- Change to the directory where you ran the docker compose (or docker run) command.
- Create a file named appsec.yaml in this directory.
- Add the following content to the
appsec.yaml
appsec_config: crowdsecurity/appsec-default labels: type: appsec listen_addr: 0.0.0.0:7422 source: appsec
Because CrowdSec runs in a container, set listen_addr to 0.0.0.0 (not 127.0.0.1) so it listens on the container’s network interface.
Mount the file in your Compose service:
services:
crowdsec:
volumes:
- /path/to/original:/etc/crowdsec # or a named volume
- ./appsec.yaml:/etc/crowdsec/acquis.d/appsec.yaml
Once you have updated the compose file to include the volume mount and the updated environment variable, you can restart the container.
docker compose down crowdsec
docker compose rm crowdsec
docker compose up -d crowdsec
With kubernetes the acquisition setup is twofolds: We have to add
appsec:
acquisitions:
- appsec_config: crowdsecurity/appsec-default
labels:
type: appsec
listen_addr: 0.0.0.0:7422
path: /
source: appsec
enabled: true
Remediation Component Setup
As stated previously this guide already presumes you have the Traefik Plugin installed. If you do not have the Traefik Plugin installed, please refer to the official documentation for installation instructions.
Configuration
Depending on how you configured the Traefik Plugin, you will need to update the configuration to include the AppSec configuration.
- Traefik dynamic configuration
- Traefik middleware (Kubernetes)
If you have defined a dynamic configuration file for Traefik, you can add the following configuration to the file.
# Dynamic configuration
http:
routers:
my-router:
rule: host(`whoami.localhost`)
service: service-foo
entryPoints:
- web
middlewares:
- crowdsec
services:
service-foo:
loadBalancer:
servers:
- url: http://127.0.0.1:5000
middlewares:
crowdsec:
plugin:
bouncer:
enabled: true
crowdsecAppsecEnabled: true
crowdsecAppsecHost: crowdsec:7422
crowdsecAppsecFailureBlock: true
crowdsecAppsecUnreachableBlock: true
crowdsecLapiKey: privateKey-foo
Instead if you define the configuration using labels on the containers you can add the following labels to the Traefik Plugin container.
labels:
- "traefik.http.middlewares.crowdsec-bar.plugin.bouncer.enabled=true"
- "traefik.http.middlewares.crowdsec-bar.plugin.bouncer.crowdsecAppsecEnabled=true"
- "traefik.http.middlewares.crowdsec-bar.plugin.bouncer.crowdsecAppsecHost=crowdsec:7422"
- "traefik.http.middlewares.crowdsec-bar.plugin.bouncer.crowdsecLapiKey=privateKey-foo"
Here's a Traefik Middleware ressource you can apply with
kubectl apply -f traefik-middleware.yaml
apiVersion: traefik.io/v1alpha1
kind: Middleware
metadata:
name: crowdsec
namespace: traefik
spec:
plugin:
crowdsec-bouncer-traefik-plugin:
enabled: true
crowdsecMode: stream
crowdsecLapiScheme: http
crowdsecLapiHost: crowdsec-service.crowdsec.svc.cluster.local:8080
crowdsecLapiKey: <shadowed>
htttTimeoutSeconds: 60
forwardedheaderstrustedips:
- 10.0.0.0/8
- 192.168.0.0/16
- 134.209.137.94
- 2a03:b0c0:2:f0::f557:a001
crowdsecAppsecEnabled: false
crowdsecAppsecHost: crowdsec:7422
crowdsecAppsecFailureBlock: true
crowdsecAppsecUnreachableBlock: true
You can still add some route configuration through IngressRoute and attach the middleware to those routes.
For more comprehensive documentation on the Traefik Plugin configuration, please refer to the official documentation.
We can't cover all the possible configurations for Traefik in this guide, so please refer to the official documentation for more information.
Directives
The following directives are available for the Traefik Plugin:
crowdsecAppsecEnabled
bool
Enable or disable the AppSec Component.
crowdsecAppsecHost
string
The host and port where the AppSec Component is running.
crowdsecAppsecFailureBlock
bool
If the AppSec Component returns 500 status code should the request be blocked.
crowdsecAppsecUnreachableBlock
bool
If the AppSec Component is unreachable should the request be blocked.
Testing the AppSec Component + Remediation Component
if you try to access http://localhost/.env from a browser, your request will be blocked, resulting in the display of the following HTML page:
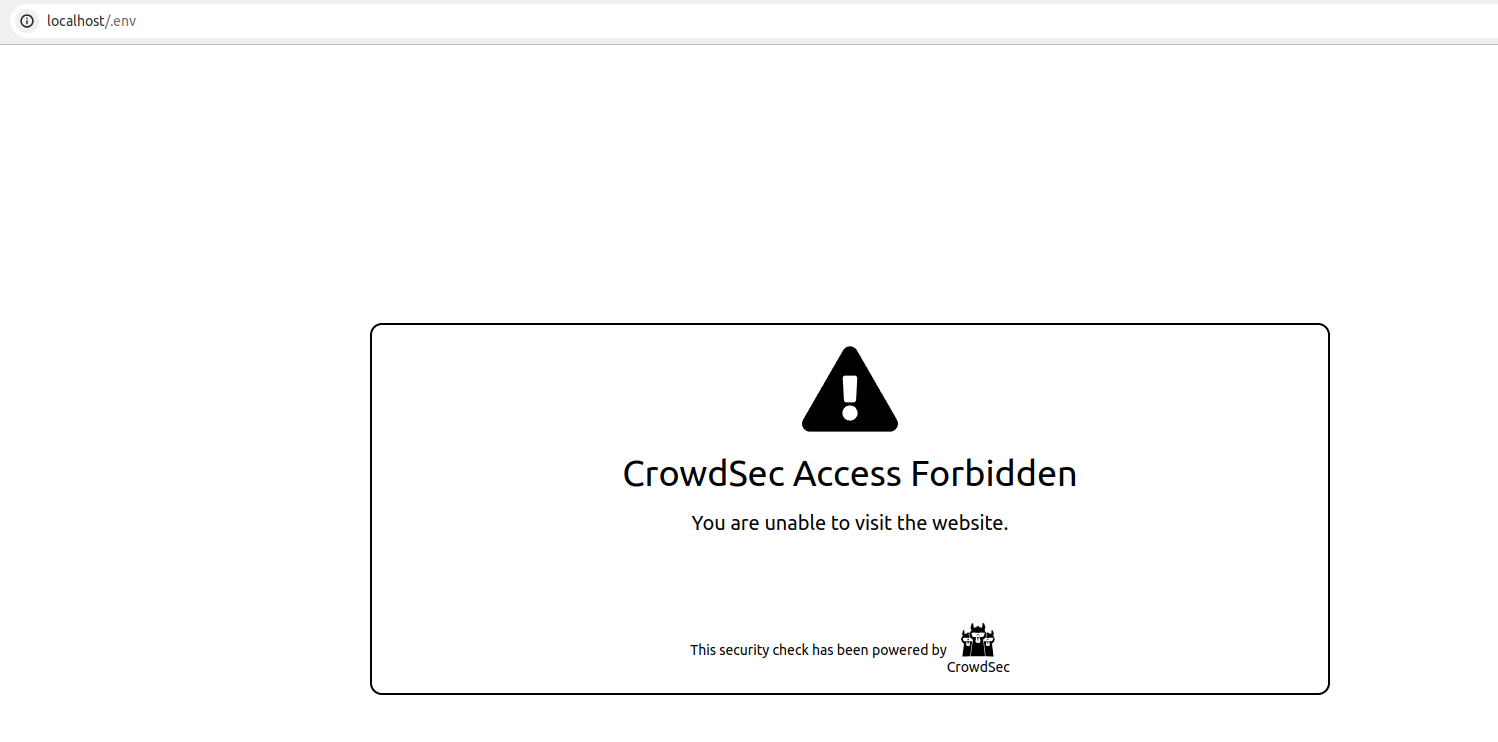
We can also look at the metrics from cscli metrics show appsec it will display:
- the number of requests processed by the AppSec Component
- Individual rule matches
Example Output
Appsec Metrics:
╭─────────────────┬───────────┬─────────╮
│ Appsec Engine │ Processed │ Blocked │
├─────────────────┼───────────┼─────────┤
│ 127.0.0.1:7422/ │ 2 │ 1 │
╰─────────────────┴───────────┴─────────╯
Appsec '127.0.0.1:7422/' Rules Metrics:
╭─────────────────────────────────┬───────────╮
│ Rule ID │ Triggered │
├─────────────────────────────────┼───────────┤
│ crowdsecurity/vpatch-env-access │ 1 │
╰─────────────────────────────────┴───────────╯
Explanation
What happened in the test that we just did is:
- We did a request (
localhost/.env) to our local webserver - Thanks to the Remediation Component configuration, forwarded the request to
http://127.0.0.1:7422 - Our AppSec Component, listening on
http://127.0.0.1:7422analyzed the request - The request matches the AppSec rule to detect .env access
- The AppSec Component thus answered with HTTP 403 to the Remediation Component, indicating that the request must be blocked
- The web server then presented us with the default "request blocked" page.
Integration with the console
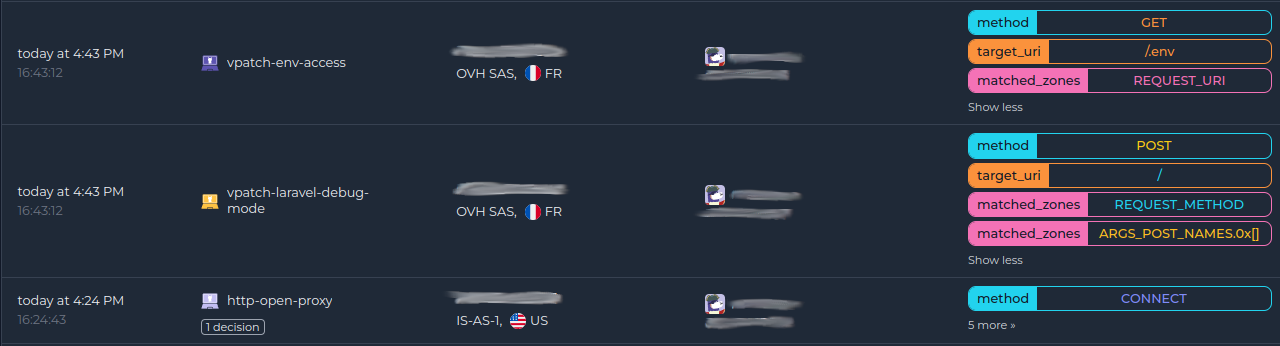
If you haven't yet, follow the guide about how to enroll your Security Engine in the console.
Once done, all your alerts, including the ones generated by the AppSec Component, are going to appear in the console:
Next steps
You are now running the AppSec Component on your Crowdsec Security Engine, congrats!
As the next steps, you can:
- Explore the hub to find more rules for your use case
- Look at the Rules syntax and creation process to create your own and contribute
- Take a look at the benchmarks

